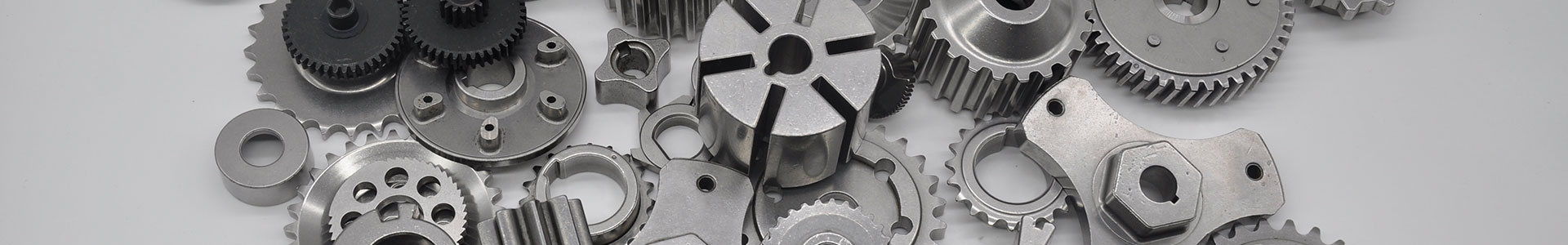
Couplings and Connectors:
Purpose: These components are used to join shafts and other moving parts in robotic assemblies.
Advantages: PM parts provide high strength and reliability, ensuring that the connections between robotic components can withstand heavy loads and repetitive movements.
Sprockets and Pulleys:
Purpose: Sprockets and pulleys are often used in robotic systems to transfer motion via belts or chains.
Advantages: Sintered parts offer precision in tooth alignment and smooth operation, which helps in the efficient transmission of force with minimal wear.
Cam and Cam Followers:
Purpose: Cams convert rotational motion into linear motion, which is a common requirement in robotic assemblies.
Advantages: PM technology allows the creation of cams with complex profiles and shapes, providing efficient motion control with high wear resistance.
Motors and Actuator Components:
Purpose: Motors and actuators in robots often rely on PM parts for core components like rotors, stators, and magnetic cores.
Advantages: PM can produce these parts with precise magnetic properties and dimensional accuracy, ensuring high efficiency and durability in robotic motor systems.
Precision Pins and Shafts:
Purpose: These parts are used to transmit motion and serve as pivot points in robotic joints.
Advantages: Powder metallurgy provides high strength, wear resistance, and the ability to create small, complex geometries that would be difficult or expensive to machine from solid metal.