Powder metallurgy (PM) plays a crucial role in the production of various parts used in industrial robots. These parts are typically chosen for their strength, wear resistance, precision, and ability to handle complex geometries. Below is a list of powder metallurgy parts commonly used in the industrial robotics sector:
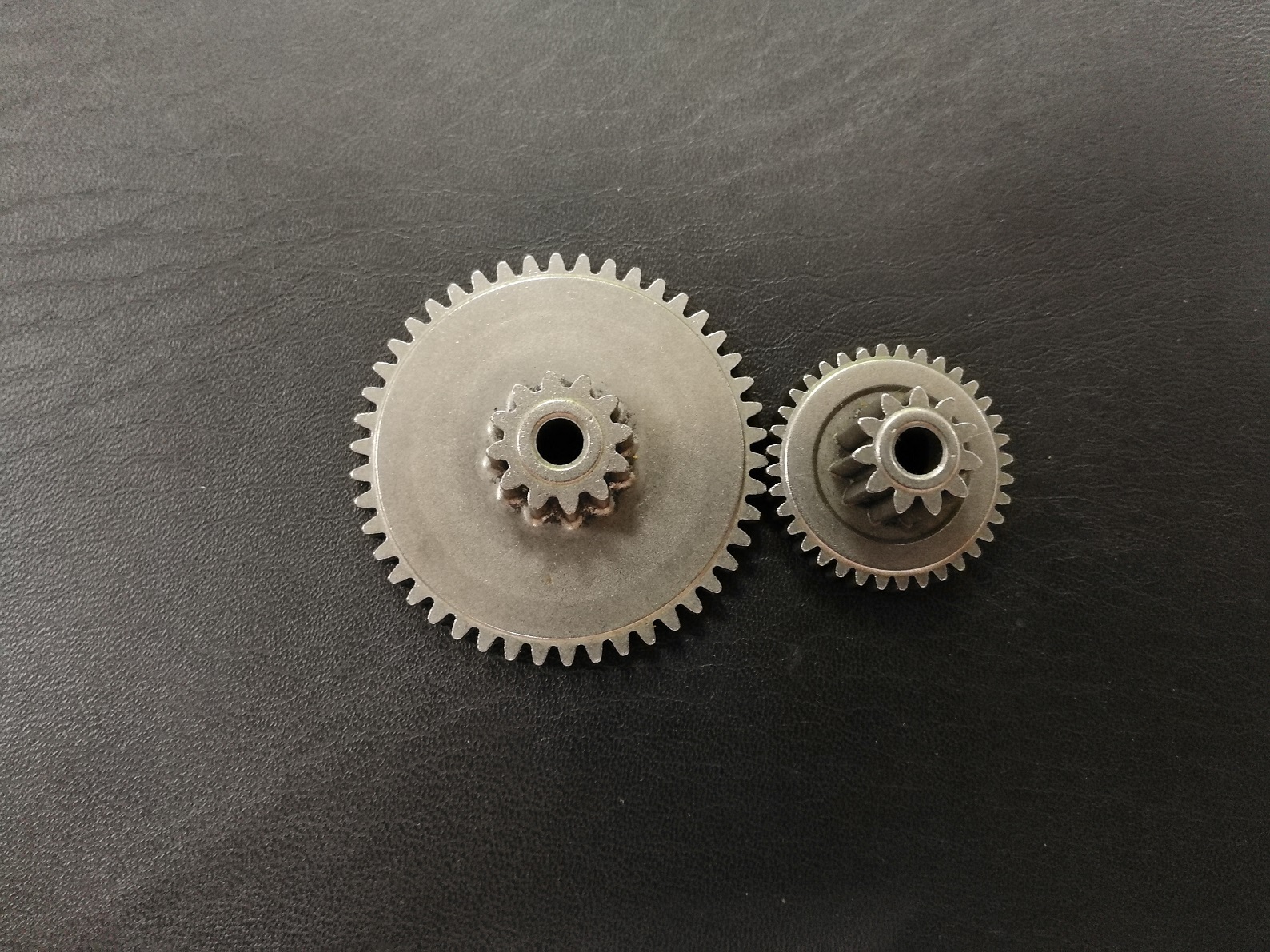
1. Gears
Planetary Gears: Used in robotic arms and actuators for precise motion control.
Spur Gears: Utilized in gearboxes and drive systems for transmitting torque.
Helical Gears: Offer smoother operation and are commonly used in high-performance robotics applications.
Bevel Gears: Used in angular motion transmission within robotic joints.
2. Bearings
Self-lubricating Bearings: Provide low friction and long life in robotic joints and rotating components.
Needle Roller Bearings: Used in compact spaces where high load capacity is required.
Sintered Bushings: Offer low maintenance and are used in pivot points and rotating parts.
3. Actuator Components
Rotor Cores: Used in electric motors for robotic actuators, made from soft magnetic composites for efficient energy conversion.
Stator Cores: Also made from magnetic materials, these components are crucial for the performance of motors in robots.
4. Structural Components
Linkages and Joints: Precision-made components that form the structure of the robotic arms and ensure smooth movement.
Mounting Plates and Brackets: Structural elements made from PM for securing various parts of the robot.
Housing Components: Enclosures and structural frames that protect sensitive internal components.
5. Clutch and Brake Components
Friction Discs and Plates: Used in robotic systems to control movement and ensure precise positioning.
Sintered Clutch Facings: Offer high wear resistance and are used in robotic drive systems.
6. Camshafts and Cams
Cams: Utilized in robotic systems to convert rotary motion into linear motion for precise mechanical operations.
Camshafts: Essential for controlling the timing and movement in robotic systems.
7. Pulleys and Sprockets
Timing Pulleys: Used in belt-driven systems for precise movement control in robots.
Sprockets: Utilized in chain-driven systems within robotic drives.
8. Magnetic Components
Soft Magnetic Components: Used in various electromagnetic devices within robots, including sensors and actuators.
Permanent Magnets: Essential for motors and sensors in robotic systems, often produced through PM methods.
9. Couplings
Flexible Couplings: Used to connect rotating shafts and accommodate misalignments in robotic systems.
Rigid Couplings: Provide strong and precise connections between components.
10. Electrical Contacts and Connectors
Contact Plates: Used in robotic control systems to ensure reliable electrical connections.
Connector Pins: Essential for ensuring the transfer of signals and power in robotics.
11. Sensors Components
Magnetic Sensor Components: Often used in proximity sensors and position encoders in industrial robots.
Shielding Components: PM parts that provide electromagnetic shielding for sensors.
12. Customized Tooling
End Effectors: Custom-designed PM parts for grippers, cutters, and other tooling at the end of robotic arms.
Precision Nozzles: Used in tasks like welding, painting, or dispensing materials by robots.
These components showcase the versatility and importance of powder metallurgy in the design and manufacturing of industrial robots, particularly in areas where high precision, durability, and complex geometries are required.